INP-WealthPk
Azeem Ahmed Khan
Regenerative farming is emerging as a practical solution to the challenges confronting modern agriculture, offering a path to improve soil health, boost productivity, and reduce environmental damage, reports WealthPK.

Loss of fertile soil, biodiversity, indigenous seeds, and traditional knowledge is threatening our ability to feed ourselves. Regenerative farming is the way forward to reverse this damage and ensure a sustainable food supply for future generations. “Regenerative farming method, if adopted widely, could significantly improve food security and sustainability, both globally and in Pakistan,” Fakhar Imam, Head of Food Security Unit at Zarai Taraqiati Bank Limited, said.
Talking to WealthPK, he said there are strong reasons to support the shift from conventional to regenerative agriculture. “The current systems overuse resources, pollute water, rely on expensive inputs, and contribute to climate change, while regenerative systems use fewer inputs, reduce pollution, and create more stable rural communities.”
Quoting soil scientists, Imam warned that if the current rate of soil damage, caused by carbon loss, erosion, desertification, and chemical pollution, continues, the world could face a serious crisis within the next 50 years. “Not only will our food become less nutritious and lack essential minerals, but we may also run out of enough fertile topsoil to grow the food we need to survive,” he cautioned.
Regenerative farming also offers economic benefits. “The organically produced food is in demand and fetches higher prices in the market. The low-income countries can also benefit, as regenerative systems require fewer costly inputs like chemical fertilizers,” he stressed. Though gaining momentum today, regenerative agriculture has historical roots dating back to early 20th-century research on soil health in the United States.
Over the years, this approach has gained global attention due to its numerous benefits. “It focuses on building a healthy soil using organic methods like composting, crop rotation, cover crops, minimum tillage, mulching, and preserving biodiversity,” Imam explained. These techniques help regenerate soil rather than degrade it, he said, adding that healthy soil means healthy food, clean water, and clean air.
By boosting soil organic matter and minimising erosion, regenerative farming enables farmers to produce more nutritious crops while enhancing the long-term productivity and resilience of their land, he added. Several methods are used in regenerative agriculture, Imam said.
One of them is Holistic Decision Making, which helps farmers make choices that are socially, economically, and environmentally responsible. Permaculture Design method enables farmers to organize their farms in harmony with natural ecosystems, enhancing both sustainability and efficiency, he said.
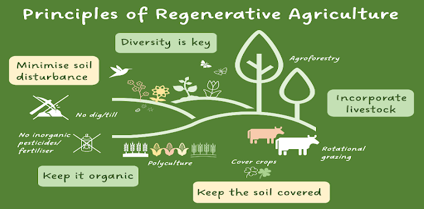
Another important method is the Soil Food Web. It is not a man-made farming method; rather, it is a natural system that has supported plant growth for hundreds of millions of years, long before the use of chemical fertilizers.” This refers to the natural system of microorganisms in the soil, including bacteria, fungi, and nematodes, which feed on plants.
They draw nutrients from the soil and deliver them directly to the roots of living plants. “With careful management of the Soil Food Web, farmers can significantly boost plant growth in a short amount of time,” Imam said. The no-till crop production method is also essential because tilling damages the beneficial organisms in the soil. Tilling involves significant physical disturbance beneath the soil surface, such as ploughing, cultivating, or using a rototiller.
“Tilling is the most harmful practice for soil organisms, even more destructive than the use of pesticides or fungicides,” he stated. Another method is the planting of perennial crops, which grow year-round and help prevent soil erosion. “Perennial plants develop deep roots over time that enable them to reach nutrients and water sources that annual plants cannot access,” Imam said.
Polyculture is yet another method, where different crops are grown together in one area to create a balanced ecosystem. An imbalanced ecosystem can result in numerous issues, including plant diseases, disruptions to insect populations, declining soil fertility, loss of wildlife habitats, and reduced crop resilience to drought and heat, he added. Thermal compost can also be used to restore microbial life in the soil.
Without these microbes, plants suffer from nutrient deficiencies, become more prone to diseases, and are less able to withstand stresses such as drought and insect attacks. “When we use all these methods, we do not just protect the environment, we actually improve it, and this is how we can create productive farms and healthier communities,” he noted.
Credit: INP-WealthPk










